Wize Alliance and Wize Techology

What is the Wize Alliance and Wize Technology?
The Wize Alliance is a non-profit association that promotes an international standard for the Internet of Things. The organization brings together major international players from the industrial and utility sectors to support the implementation of Long Range Wide Area Network Technology called Wize.
Who Founded the Wize Alliance and why?
The Wize Alliance was founded by SUEZ, GRDF, and Sagemcom, to secure the durability and sustainability of the WIZE technology and to export the technology and enter new markets, particularly Smart Cities.
Additional reasons as to why the Wize Alliance was formed include:
- Improving interoperability between connected objects using low power wide area networks.
- Educating the Internet of Things market and promoting the applications and benefits of the WIZE technology.
- Establishing a sharing environment between its various members to enhance the WIZE technology, and participate in its development, particularly through the standardization work such as those setup on the 13757-x European Standard.
- Identifying and coordinating a network composed of start-up, developers, and WIZE technology compliant product suppliers to provide a wide range of interoperable products.
The History Behind The Wize Alliance
The Wize Alliance and Wize Technology was officially launched in March 2017. Due to the expertise and business of it’s founding members, SUEZ, GRDF, and Sagemcom, wireless metering of water and gas was the starting point for the Wize Alliance. The alliance has grown since then to include 40 + members operating in a number of different industries: Energy and water grid operators, transmission and distribution operators, equipment, semiconductor and battery manufacturers, information systems and complex industrial system integrators, security experts, academics, wireless technology experts, start-ups, and more. Radiocrafts is a member of the Wize Alliance.
With the rapid growth of the Wize Alliance, they have been able to expand into new markets such as:
- Urban transport
- Public Lighting
- Connected Factories
- Wastewater Treatment
- Waste Management
- and other Smart City applications
The Wize technology continues to expand into new markets, particularly in Smart City.
Wize Alliance Success Story
Wize technology’s basics have been implemented and industrialized since 2005, the first deployments being automated meter reading (AMR) for water meters. It has been successfully deployed and operated by cities and professionals for more than 10 years. Since 2019, Wize technology connects more than 3 million water meters and will be enabled for 11 million communicating gas meters by 2022. More than 500 cities across 15 countries use it.
Since 2019, networks using Wize technology connect over 6 million objects worldwide in various Smart Metering and Smart City applications and continue to expand.
The WIZE Technology
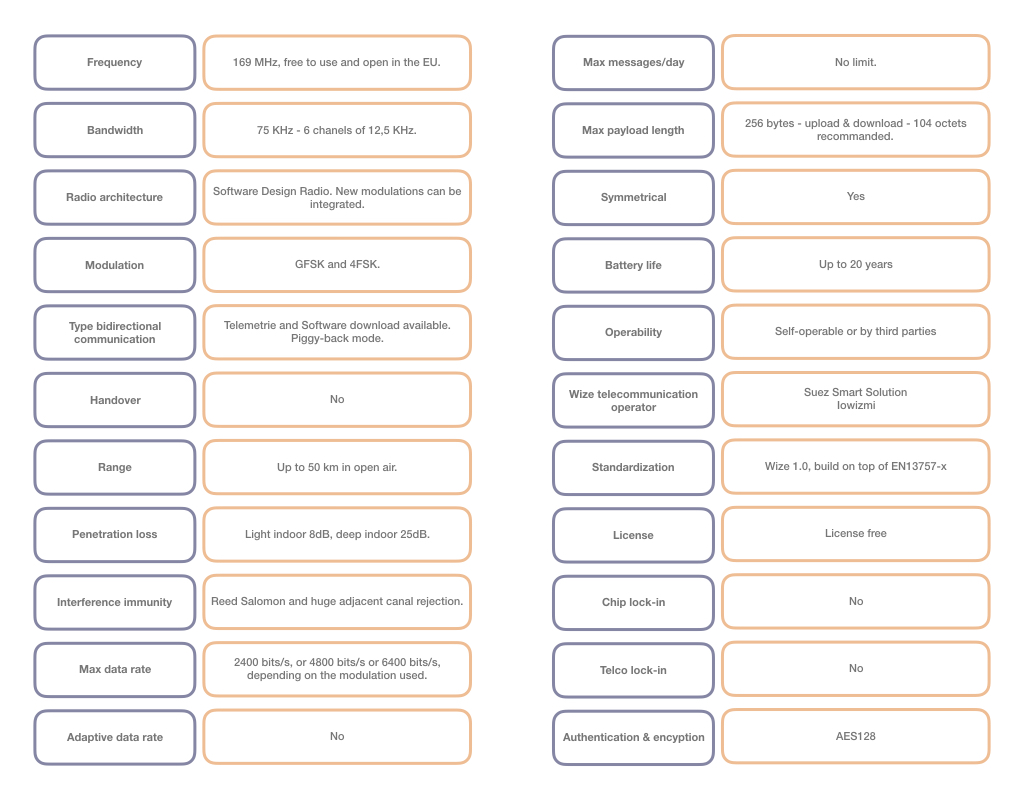
Wize is a 169 MHz IIoT technology designed to achieve long range, great object penetration, and long battery life. It is based on Wireless M-Bus mode N which has been used in millions of gas and water meters in commercial operation for several years. Wize has several benefits which include:

Based on a Proven European Standard, 13757-x
Designed For Hard-To-Reach Areas

Simple Deployment Requirements

Low Maitenance

A Non-Populated Spectrum

Over-The-Air updates
- Based on a European Standard – The current version of Wize is based on the European standard 13757-x, defined by the European Union to accompany the deployment of communicating meters. Since the launch of the Wize Alliance and Wize Technology in 2017, the standard is open to other use cases for IoT. Read our whitepaper on the relationship between Wireless M-Bus and WIZE.
- Designed For Hard To Reach Places – The Wize technology operates in the 169 MHz ISM Band which allows for good RF performance in terms of building penetration (low building penetration loss), coverage (range of 50km Line of Sight), and consumption of battery. Specifically designed to connect hard to access objects, Wize delivers secure information for Internet of Things applications for cities, industrial or tertiary sectors.
- Field Proven – Using their 13 years of experience, the Wize Alliance has deployed 6 million Wize enabled devices in the field, in 15 countries and 500 cities. The Wize Alliance predicts that by 2021 there will be 15 million Wize enabled devices.
- Simple Deployment Requirements – The deployment of the network is simple and fast because the technology requires a minimum of equipment (a communicating object and a concentrator): no repeater system, no pairing or complex programming sensor. The technology is already proven in many countries in Europe and Africa and it is rather easy to deploy a network on a local scale.
- Low Maintenance – The Wize technology can connect to devices which energy-efficient enough to last a very long time. Additionally, since the technology requires a minimum of equipment, it facilitates the operating and maintenance costs.
- A Non-Populated Spectrum – Communications from one object to the gateways are carried out in broadcast mode in both directions which allows multiple gateways to receive the same message from an object. Therefore, this system increases the performance of the radio solution by providing redundancy and high availability in the system.
- Fast Firmware Rollout – bi-directional communication and over-the-air updates are supported by Wize.
- Reliable – No dependence from any telecom operator network.
169 MHz ISM Band
Many of the benefits of using Wize, or Wireless M-Bus at 169 MHz, comes from the radio properties. The range and therefore the radio area coverage come as a result of combining several features:
- Narrowband radio, using 12.5 kHz channels increase the sensitivity
- Low data rate (2.4/4.8/6.4 kbps) increase sensitivity
- Narrowband radio also improve the selectivity, reducing interference and blocking
- High RF transmission power, up to 500 mW of radiated power is allowed in this band and increase the range
- The relatively low frequency at 169 MHz gives good penetration in buildings and deflects around obstacles
- The relatively low frequency yields a lower path loss due to larger antenna area (but means the antenna structure will be larger)
Read more about this in our Wize Protocol White Paper.
Wize Technology Existing Use Cases
The Wize technology has been used predominantly in Smart Metering, but what other existing use cases use this technology?
Automatic and remote water cut-off:
Hydrelis have come up with a solution to switch off water supplies within buildings automatically and remotely in case of a leak, this solution is used by Suez in its ON’Connect™ switch solution. The device provides real-time prevention of suspected leaks and sends automatic alerts mitigating water damages.
Furthermore, the automatic and remote management of water supplies of buildings, depending on usage (weekends, nights, holidays, etc.) empowers consumers to reduce their water consumption and to lower their bill by up to 30%. The solution is connected to Wize networks already installed in many cities.
Leak detection with acoustic data loggers:
Sewerin have developed a way to detect water leaks in real-time using the 169 MHz frequency band and acoustic zone monitoring sensors. The data loggers are placed in underground water networks where they are used to record noise. When a change in the recorded noise data is detected, this means there is a leak.
These acoustic data loggers have allowed water companies to monitor their network remotely and in real-time. The 169 MHz frequency band has proven to be a good choice as the water networks are buried underground.
These and many many more use cases are possible with Wize!
Radiocrafts Wize RF Module For Hard-To-Reach Areas
Radiocrafts RC1701HP-WIZE module is a 169 MHz IIoT technology designed to achieve long range, great object penetration, and long battery life. It is based on Wireless M-Bus mode N which has been used in millions of gas and water meters in commercial operation for several years. It is specially designed for deployments on a territory-wide scale which require integration in a constrained environment: metering, public lighting, energy management of buildings, smart mobility, etc.


