Cloud computing is gaining popularity as more and more businesses are launching public and private cloud computing initiatives. In fact, the cloud computing industry is one of the fastest growing today. According to Gartner, a leading research and advisory company, the revenue for global public cloud services is forecasted to reach $411.4 billion in 2020. With the growth of the cloud computing industry, comes the growth and diversification of opportunities available for an astounding amount of industries.
 Some of the top industries leveraging cloud computing include the IoT industry, automotive industry, entertainment industry, retail industry and many, many more. Cloud computing is still a new phenomenon in the world today, and, just like with most new things, there are opportunities for improvements. A challenge in cloud computing for the IoT industry we will be focusing on is in cloud development, and more specifically, that there is a lack of access to real sensor networks in the development phase for cloud developers.
Some of the top industries leveraging cloud computing include the IoT industry, automotive industry, entertainment industry, retail industry and many, many more. Cloud computing is still a new phenomenon in the world today, and, just like with most new things, there are opportunities for improvements. A challenge in cloud computing for the IoT industry we will be focusing on is in cloud development, and more specifically, that there is a lack of access to real sensor networks in the development phase for cloud developers.
Therefore, in this blog topic we will first give you an introduction to the “cloud” and “cloud development”. We will then discuss the relationship between IoT and cloud. Furthermore, we will discuss the lack of access to real sensor networks for cloud IoT developers and how real data compares to simulated data when creating a sensor network for their cloud IoT application. Finally, we will introduce the Cloud To Sensor Prototype Network by RIIM as a Radiocrafts solution to tackle this issue.
The Cloud and Cloud Development
What we know as the cloud in the IoT industry is not the weirdly-shaped pockets of condensed water in the sky, but rather, a powerful combination of cloud computing, networking, storage, management solutions and business applications that facilitate consumer services. Simply put, the cloud involves storing and accessing data and programs over the internet instead of on your PC’s hard drive. Essentially, with an online connection, cloud computing can be done anywhere.
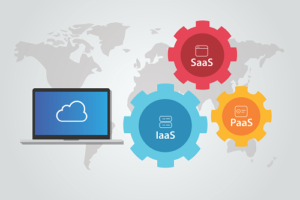
There are different kinds of cloud services for business. Some businesses choose to implement Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) where the business subscribes to an application it accesses over the internet. Salesforce is an example of a SaaS. Other businesses choose to implement Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) where a business can create it’s own cloud application for use by everyone in the company. And Finally, there is Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) where large players like Amazon and Microsoft provide a back-bone cloud service that can be rented out by other companies. For example, you are able to watch your favourite shows on Netflix because it’s a customer of the cloud services at Amazon.
Cloud development involves, well, developing the cloud. However, developing the cloud is not as simple as you might think. This involves developing the cloud architecture such as planning, organizing, and designing to implementing and structuring cloud delivery models (Iaas, Paas, Iaas). Additional tasks in cloud development include managing the cloud service delivery models. This involves connecting outside provider data centers back to your company’s network, creating a recovery plan in case the cloud service goes down, network bandwidth and more. Furthermore, there is the cloud software development which comprises of designing and developing cloud applications, services, and products. This can include anything from back-end, front-end, web application, full-stack, data and application integration and cloud application deployment.
Relationship Between IoT Industry And The Cloud
The IoT industry and cloud computing industry are one of the fastest growing industries in the world at the moment. Although both have completely different functionalities, they are symbiotic in nature and work best in unison. Why is that? Allow us to explain.
IoT devices such as sensors and actuators generate and use an astonishing amount of data, putting an immense pressure on the internet infrastructure. The cloud provides a way for companies to store, process, and transfer this intense amount of data in the cloud instead of in the devices themselves. To provide you with an example of this, you can have hundreds of thousands of sensors installed in a farm to monitor crops. These sensors gather data continuously, which needs to be analyzed later on. However, analyzing the immense amount data coming from hundreds and thousands of sensors can be a daunting task as it takes large amounts of computational power, energy, and money to analyse data from each individual sensor. That is where the cloud application comes in handy, storing all the data and creating rule engines and algorithms to provide estimated results of those data points. As you can see, the IoT and the Cloud have a beautiful Leonardo di Caprio and Kate Winslet kind of relationship.
The IoT and Cloud Computing have become the two most closely associated future internet technologies, which has accelerated the development and deployment of scalable IoT applications and business models.
However, as previously mentioned, the cloud and cloud development are a new phenomenon in our world today which comes with its flaws as well. In this blog topic, we will talk about one particular improvement area related to the IoT which is the lack of access for cloud developers to real sensor networks in the development phase of their cloud application. We often see cloud developers using simulated sensor data as opposed to real sensor data when developing their cloud application.
Lack of Real Sensor Networks For Cloud Developers During The Development Phase of Their Cloud Application
The lack of access to real sensor networks comes from the need for cloud developers to, for example, have a real network installation in a real building to get real data. Emphasis on the REAL. Real data can be hard to get if you do not have access to these certain requirements. Working with simulated data from a computer is NEVER the same as working with real data.
Most values in simulated data are programmed as ideal values or values you would attain in a perfect world which is impossible to achieve and often inaccurate compared to actually collecting this data through experimentation of a real sensor network. Many cloud developers need a small prototyping environment where they have the freedom to make early stage errors to not cause a real building to perform poorly, for example, turning on the air conditioner in the middle of winter. These errors are much harder to identify when using simulated data rather than real data as the simulated data is not nearly as accurate as real data.
Radiocrafts has a solution to allow cloud developers to use real sensor networks when developing their cloud application. The solution is called Cloud To Sensor Prototype Network by RIIM.
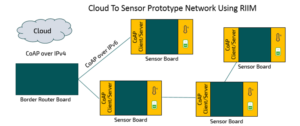
Cloud To Sensor Prototype Network by RIIM
The RIIM network from Radiocrafts is an excellent platform to get real sensor data for your IOT cloud development. Each sensor is accessed using CoAP over IPv4, making the Cloud application generic in terms of target sensor network. Once the network is set up, then each sensor can be accessed by the Border Router via IPv4 over Ethernet.
The tools you need to create your prototype sensor network include:
· A Border Router
· Sensor Boards (as many as you want)
· The SDK Software
· Antennas
· USB cables
· Power adapters
The Border Router Board has an IPv4 interface over Ethernet and is ready to go out of the box. You can access any sensor in the network and forward the data to your cloud application. The Sensor Boards are populated with 7 industry standard sensors. You can view the sensors included on the sensor board here.
The RIIM Network is a fully automatic setup (mesh topology) using the pre-loaded firmware on the boards.
The Boards come pre-configured for sensor readings. However, the pre-loaded firmware configuration of the radio and/or the sensor readings can easily be modified using any text editor and the RIIM SDK.
Additional benefits of the RIIM network include:
· “Global” support – software configurable 868/915 MHz
· You can have up to 1000 sensor boards in the network.
· Very low power operation
· 200-meter range between nodes in an urban environment
· 29 mesh hops supported which allows the network to cover an area of up to 12 x 12 km squared in an urban environment.
· It is based on established RF standards such as IEEE802.15.4g/e, CoAP, RPL, TSCH, 6LoWPAN and more.
In its simplest configuration all you need to do is to define the IP address of the cloud application and power up the boards. Once setup, you can configure the Sensor Boards to read any combination of sensors present on the board. The Border Router can then access each sensor via IPv4 over Ethernet and forward the sensor data to your cloud application, and you are done!
Read more about the Sensor To Cloud Prototype Network By RIIM here.
What To Take Away From This?
What you should take away from this blog post is that Cloud computing is still a new phenomenon in the world today which is growing rapidly in conjunction with the IoT industry. Cloud computing and IoT work hand-in-hand to assist in creating a brighter tomorrow. In this relationship sensors and actuators are able to collect vast amounts of data and store them in a cloud application for analysis. Then, an educated and well studied decision can be made from this analysed data to improve conditions, whether it be in an office, at home, or anywhere else. For Cloud developers especially, it is vital to setup a sensor network installation to collect real sensor data rather than simulated data. This way, the cloud developer allows himself to make early errors and respond to those errors in an accurate manner in the development phase. One option for cloud developers to collect real data for their development is a Radiocrafts solution known as RIIM.



Thanks for providing great information and a beautiful blog, really nice required information and things I never imagined, and I would like to request that you write more blogs and blog posts like that for us. Thank you once more.
Thanks for providing great informatic and looking beautiful blog, really nice required information & the things I never imagined, and I would request, wright more blog and blog post like that for us. Thank you once again
by Cognex
(https://www.cognextech.com/aws-training-and-certification-course-3)
Hi Cognextech2019,
Thank you for your kind feedback. We are always looking to write blog items that provide a fun learning experience for our web visitors that are relevant to the current state and future of the IoT industry. Stay tuned for more content coming your way!
Kind Regards,
Radiocrafts Team